In the past, Switzerland has always distinguished itself by its ability to adapt. Now it is in danger of missing a decisive transformation.
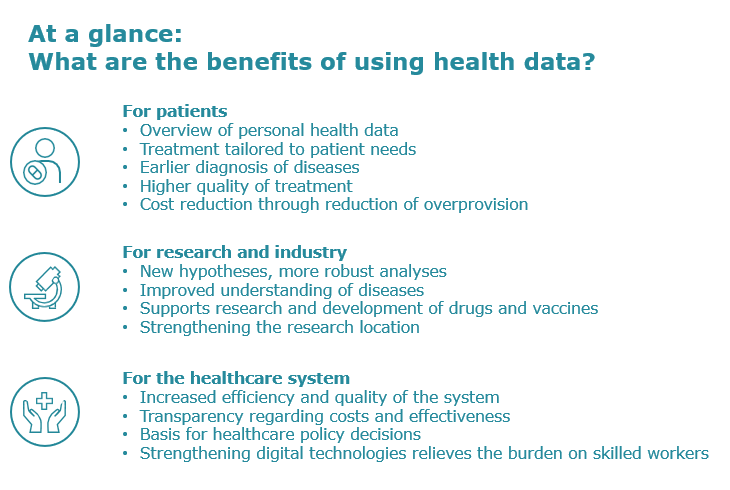
Throughout the life cycle of a drug, data helps us to better understand diseases, develop more targeted therapies and provide individual support to patients. Drug approval, reimbursement and treatment decisions are based on data.
Data from healthcare providers makes it possible to gain a better understanding of the health, quality of care and treatment needs of the Swiss population. In addition to clinical results – such as blood values, imaging data, results of functional tests or complication rates – patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) relating to the patient should also be collected. These record quality of life from the patient’s perspective. This data should mandatorily be recorded using standardized processes and instruments and integrated into the treatment plan in order to obtain a comprehensive overall picture. This information can contribute to the continuous and dynamic improvement of healthcare, in the spirit of a “learning” healthcare system.
Secondary use
When you visit a pharmacy, doctor’s office or hospital, health data is recorded in information systems. These systems exist to ensure safe treatment, but they can also advance the field of medicine more generally. Using the data from many patients makes it possible to improve prevention, diagnosis and treatment, as well as to develop more effective monitoring mechanisms for the healthcare system.
This re-use of data previously collected for other purposes is called secondary use. This includes research, quality assurance, health statistics and planning. Data protection, transparency and the consent of the data subject are key prerequisites for secondary use. This requires clear legal and organizational rules as well as effective security measures. The federal government is currently drafting a framework law to define rules for secondary use of personal data in Switzerland that go beyond the existing laws and regulations.
Data security
Health data is highly sensitive – protecting it is a top priority. Healthcare facilities therefore use both technical and organizational measures to protect data. These include encrypted storage and transmission systems, secure authentication procedures and clearly defined access rights that ensure that only authorized persons can view or edit data. The logging of all data accesses, regular security checks and staff training are also necessary to prevent misuse and unintentional data leaks.
In Switzerland, data use is subject to the Data Protection Act (FADP) and healthcare law, which stipulate that data may only be used for specific purposes, and in a traceable and confidential manner. Patients also have the right to information and to have their data corrected.
Anonymization and de-identification
Health data may only be used for secondary purposes if the protection of privacy is maintained. This requires anonymization or de-identification. Anonymized data no longer allows conclusions to be drawn about individual persons; in the case of de-identified data, by contrast, identifying features such as names or OASI numbers are removed or encrypted.
Strict anonymization and de-identification requirements for handling health data apply both internationally and in Switzerland. In Switzerland, the Data Protection Act (DSG) and the Human Research Act (HRA) stipulate that health data for secondary use may only be used in anonymized form or with strictly controlled re-identification. Re-identification is only permitted via authorized bodies and in clearly justified cases. This strikes an appropriate balance between data protection, trust and scientific progress.
Real World Data
The enormous progress that has been made in digitalisation has opened up access to medical data which, in contrast to data from conventional clinical trials, are generated in the patient’s everyday setting. This is known as real world data (RWD).
RWD have a wide range of uses, from assessing the safety and efficacy of therapies and risk-benefit assessments for certain diseases, to complex diagnoses and conclusions about patterns and striking features in specific patient groups.
The recruitment and participation of patients in clinical trials can also be facilitated by RWD. Hospitals can select suitable participants faster and better using their own patient data. Smartphone apps and wearables help patients to record and transmit their health data wherever they are, thus reducing the number of hospital visits.
Creating fair conditions
The use of RWD in research can only be beneficial, however, if the data are of high quality, obtained under defined conditions and evaluated carefully. Here, there is a need to create a framework that ensures fair compensation for the major effort involved in generating and curating this kind of data and for the innovations that RWD make possible. Data intended to promote health should be widely available. At the same time, compliance with data protection regulations must be ensured. The effort involved in generating, curating and making the data available must be rewarded and the necessary awareness of the different types of RWD must be created. On the one hand, there are RWD that are obtained almost as a by-product under uncontrolled conditions, and on the other, there are RWD that need to fulfil very high quality requirements. RWD obtained specifically for clinical authorisations should be accorded protection similar to that given to conventional clinical data.






 read more
read more Read more articles
Read more articles Download
Download Show all publications
Show all publications

 PDF german
PDF german Go to store
Go to store read more
read more